Critical Success factors for project success
Projects are considered as successful, if they are completed on time, within budget, met the scope and achieved the business objectives of the project. How do we really achieve Poject sucess?
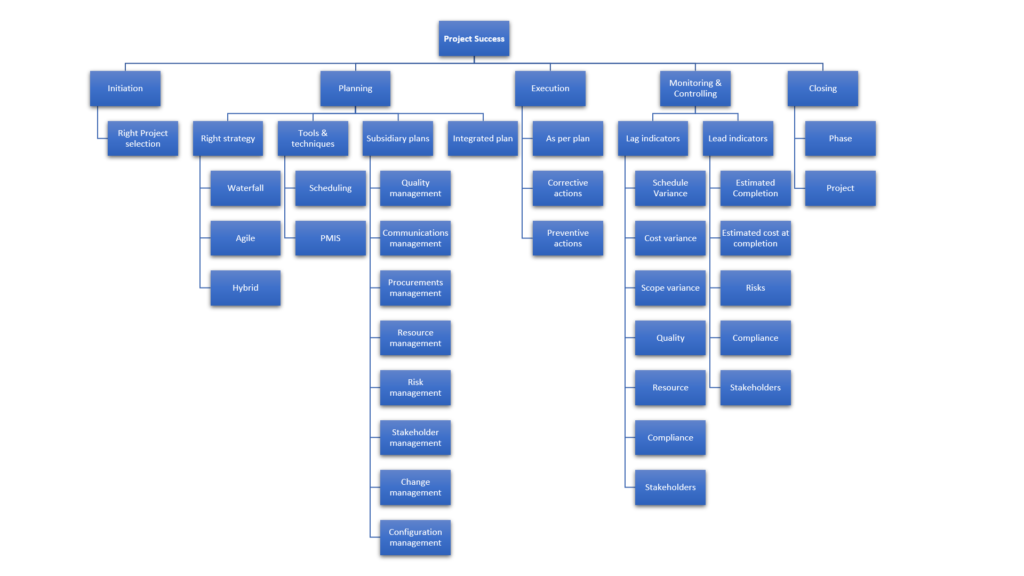
Initiation
- Right Project Selection – If the project does not have a strong business case, it will fail eventually
Planning
- Right project execution strategy (Agile, Waterfall, Hybrid) – A wrong project execution strategy can fail a project. For example, projects where scope is not clear, techno;ogy is new calls for agile / iterative development, till there is clarity. Once clarity is established, the rest of the project can follow waterfall or hybrid.
- Right tools & techniques (Scheduling, Estimation, Project Management Information Systems) – On many occassions projects fail becuase the right tools are not used effectively.
- Developing the subsidiary plans – Generally speaking, nothing good happens in projects without proper planning. For project success, one need to plan the following;
- Quality management plan
- Communications management plan
- Procurement management plan
- Resource management plan
- Risk management plan
- Schedule management plan
- Stakeholder management plan
- Change management plan
- Configuration management plan
- Developing the integrated project plan – For monitoring and controlling at a project level, all the subsidiary plans and the various other lower level plans must be integrated into a cohesive integrated project plan.
Execution
- Executing the project as per the plan
- Corrective and preventive actions
Monitoring & Controlling
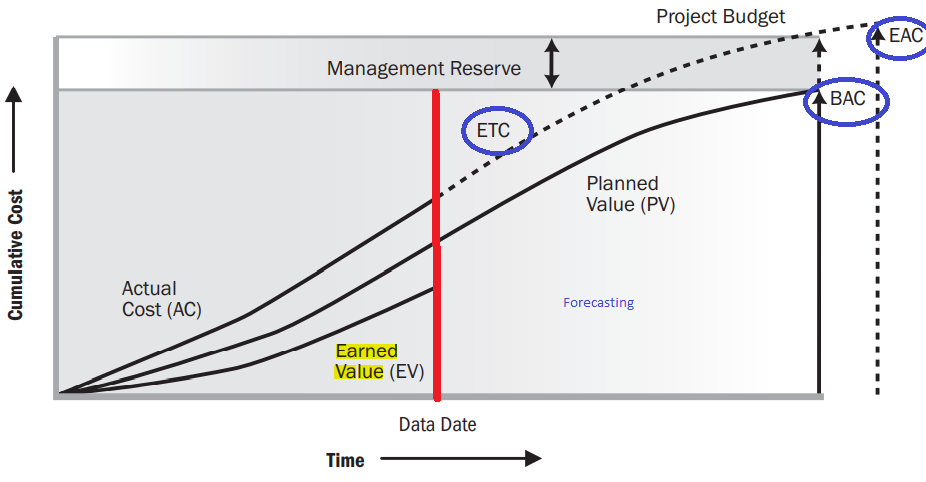
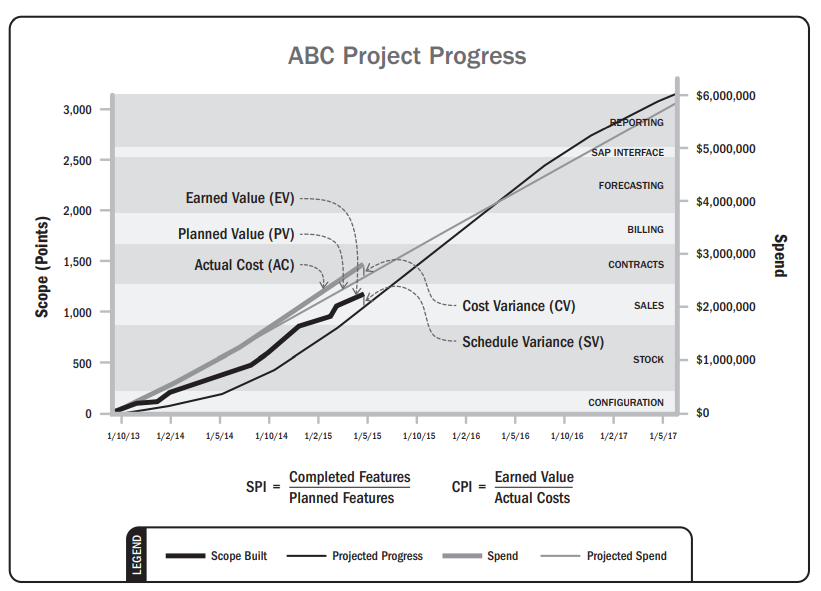
- Lag indicators
- Schedule variance
- Schedule performance index
- Cost variance
- Cost performance index
- Scope variance
- Quality issues
- Risks occured
- Lead indicators
- Estmated date of completion (work package, milestone, project)
- Estimated cost at completion
- Anticipated risks
Closing
- Closing phase
- Closing project
A quick look at the PMP certification
- Project Management Professional (PMP) is the most popular project management certification in the world. Right now, there are more than 1400000 PMP certfied professionals across the World. According to PMI Survey, PMP certified project professionals earn 16% more than their counterparts who are not PMP Certified.
- The PMP certification is based on the Project Management Body Of Knowledge (PMBOK) by Project Management Institute (PMI,USA) . The PMBOK covers;
- Predictive Project Management (Waterfall)
- Agile Project Management (Adaptive)
- Hybrid Project Management
- Before applying for the PMP Certification, it is mandatory to attend 35 hours of formal project management training based on PMBOK.
Eligibility
- Four-Year College / University Degree
- 36 months of experience leading projects within the past eight years
- 35 hours of project management education/training or CAPM® certification
OR
- High School or Secondary School Diploma
- 60 months of experience leading projects within the past eight years
- 35 hours of project management education/training or CAPM® certification
Exam content
People (42%)
- Manage conflict
- Lead a team
- Support team performance
- Empower team members and stakeholders
- Build a team
- Address and remove impediments
- Negotiate
- Collaborate with stakeholders
- Build shared understanding
- Engage and support virtual teams
- Define team ground rules
- Mentor relevant stakeholders
- Application of emotional intelligence to improve team performance
Process (50%)
- Execute project with the urgency required to deliver business value
- Manage communications
- Assess and manage project risks
- Engage stakeholders
- Plan and manage budget and resources
- Plan and manage schedule
- Plan and manage quality
- Plan and manage scope
- Integrate project planning activities
- Manage project changes
- Plan and manage procurements
- Manage project artifacts
- Determine appropriate project methodology
- Establisg project governance structure
- Manage project issues
- Ensure knowledge transfer
- Plan and manage project/phase closure or transitions
Business environment (8%)
- Plan and manage project compliance (EHS)
- Evaluate and deliver project benefits and value
- Evaluate and address external business environment changes for impact on scope
- Support organizational change
Why do PMP certified professionals earn 16% more than their counterparts?
- They understand the critical parameters that must be monitored and controlled for project success
- They understand the building blocks and their inter-relationships for monitoring and controlling the lead and lag indicators
- They understand the need for Project Management Information Systems
- They understand the globally accepted project management vocabulary, hence can communicate better
- PMP certification is an endorsement for minimum viable professional project management knowledge to be effective in larger projects
Preperation for PMP with a right balance of theory and practice will tremendously crash the learning curve to master professional project management based on a globally recognized standard (PMBOK).
To learn more about the PMdistilled PMP Preperation Program, Click here