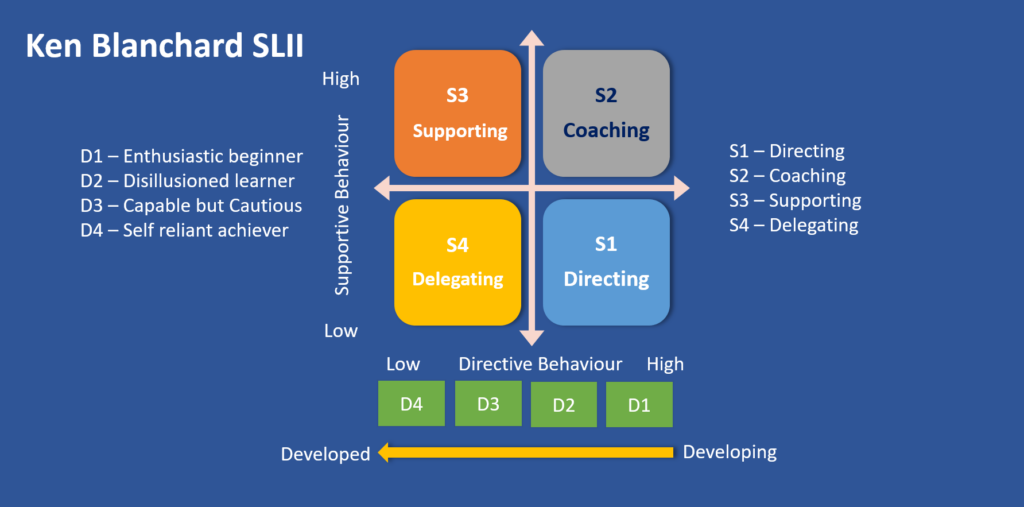
The fundamental principle of the situational leadership model is that there is no single “best” style of leadership. Project teams or project stakeholders belong to various experience levels and attitudes. Hence, there is no single style managers and leaders can adopt that will be effective across team members. These models helps to tailor one’s leadership style to cater to the needs of the individuals and teams.
One cannot have a one for all kind of leadership style for all team members in the team as they fall on to the various levels of Maslow’s hierarchy of needs. Based on their capability and maturity the leader has to change his leadership style. The basic principle of situational leadership is this. Based on the maturity level and the capability of the team members, the leader resorts to any one of the following styles of;
- Telling or Directing
- Selling or Coaching
- Participating or Supporting
- Delegating
This is a model created by Paul Hersey and Ken Blanchard.
Situational Leadership emerged as one of a related group of two-factor theories of leadership.
These theories are based on two main variables of task and relationship.
Effective leadership is task-relevant, and the most successful leaders are those who adapt their leadership style. They adapt their leadership style to the performance readiness (ability and willingness) of the individual or group they are attempting to lead or influence.
Ken Blanchard’s Situational Leadership II measures project team member development using competence and commitment as two parameters.