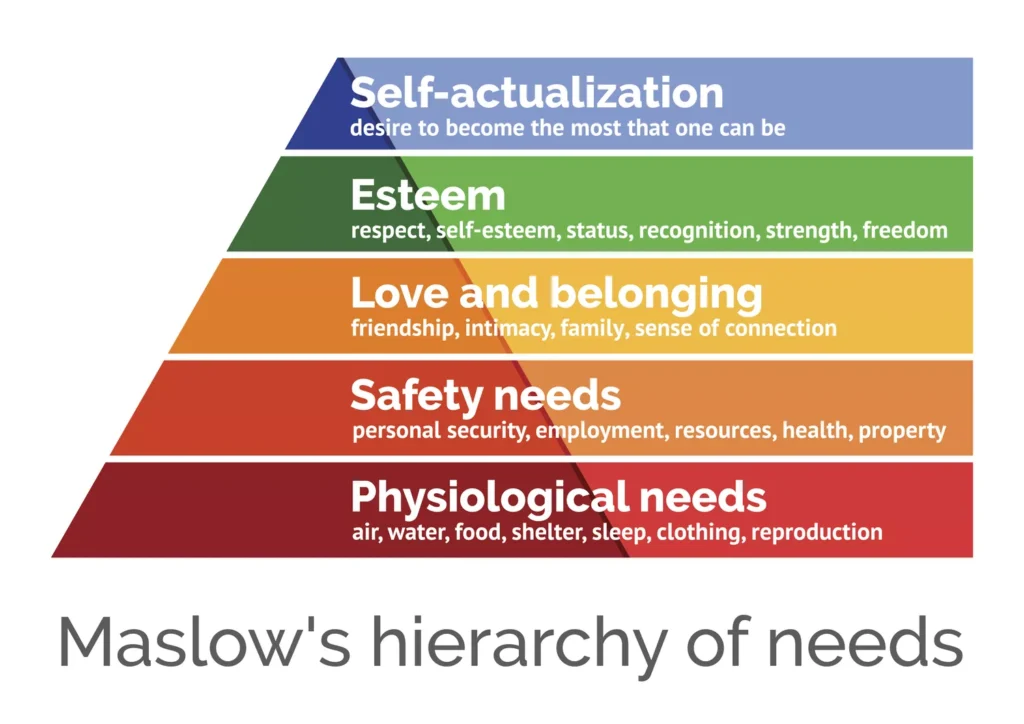
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs is a motivational theory in psychology proposed by Abraham Maslow. It is typically depicted as a five-tier pyramid of human needs, arranged from the most basic to the most advanced. Here’s a breakdown of each level:
1. Physiological Needs (Base of the Pyramid)
These are the basic necessities for human survival:
- Food
- Water
- Shelter
- Sleep
- Air
2. Safety Needs
Once physiological needs are met, individuals seek safety and security:
- Personal security
- Health and well-being
- Financial security
- Safety from accidents and injury
3. Love and Belonging Needs
Humans are social beings and seek relationships:
- Friendship
- Intimacy
- Family
- Social groups
4. Esteem Needs
After love and belonging, people desire respect and recognition:
- Self-esteem
- Achievement
- Status
- Recognition from others
5. Self-Actualization (Top of the Pyramid)
This is the realization of a person’s potential and self-fulfillment:
- Personal growth
- Creativity
- Pursuit of inner talent
- Peak experiences
Maslow suggested that individuals move through these levels sequentially, starting with the most basic needs. Only once the lower needs are satisfied can higher-level needs be pursued effectively.
