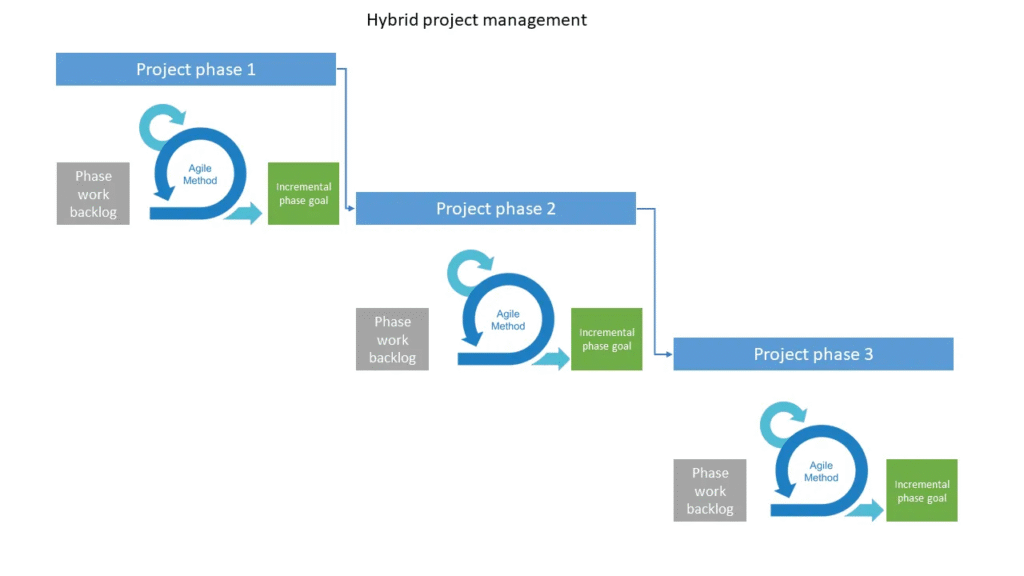
Hybrid project management is a methodology that combines elements from different project management approaches to suit the unique needs and characteristics of a specific project. It typically involves integrating traditional (waterfall) project management practices with agile methodologies to capitalize on the strengths of each approach while mitigating their weaknesses. Let’s explore how hybrid project management can be applied in both IT projects and EPC (Engineering, Procurement, and Construction) projects:
- IT Projects: In IT projects, the need for flexibility and adaptability often clashes with the structured nature of traditional project management methodologies like waterfall. A hybrid approach can blend the predictability of waterfall with the flexibility of agile methodologies. Here’s an example:Imagine a software development project where the overall project plan follows a waterfall approach, with clear milestones and deliverables defined upfront. However, within each phase of the waterfall model, agile practices such as iterative development, frequent reviews, and continuous integration are employed.For instance, during the requirements gathering phase, the project team uses traditional techniques to document and finalize requirements. Then, during the development phase, the team adopts agile practices like Scrum or Kanban to iteratively develop and deliver software increments. Regular sprint reviews and retrospectives allow for continuous feedback and adjustments, ensuring that the project stays aligned with evolving stakeholder needs.
- EPC Projects: EPC projects, which involve complex engineering, procurement, and construction activities, often require a balance between meticulous planning and the ability to respond to unforeseen challenges. A hybrid approach can integrate elements of both traditional project management and agile methodologies to enhance project efficiency and adaptability. Here’s an example:Consider a large-scale construction project, such as building a new power plant. The project may begin with a detailed design phase following a traditional waterfall model, where the engineering requirements are thoroughly planned and documented. However, during the construction phase, the project team may encounter unexpected site conditions or supplier delays, necessitating agile responses.In this scenario, the project manager might implement agile principles such as daily stand-up meetings, adaptive planning, and rapid decision-making to address emerging issues and keep the project on track. For instance, if a critical equipment delivery is delayed, the project team can quickly adjust construction schedules and resource allocations to minimize the impact on the overall project timeline.
By integrating traditional and agile project management practices, hybrid project management offers a flexible and pragmatic approach to addressing the diverse challenges inherent in IT and EPC projects, ultimately enhancing project success and stakeholder satisfaction.
