What is project scope management?
Assume that you want to construct a house. Where do you start?. You start dreaming or thinking about it. Then you sketch it. Discuss with others. Refine the sketch. Appoint a consultant to detail it for you. He comes out with the high level layout. Which goes through multiple iterations, till the final plan is approved by you and your family. Then he gets into the detailed layout. At this stage a construction contractor is identified. He comes out with the detailed engineering drawings for civil work, plumbing and electrical if all these are done by the same person, or else each of these may have different contractors or sub-contractors.When all the detailing is done and approved by the owner, The work breakdown structure is prepared, and the scope gets base lined. There after any changes to the scope will have to follow the change management process and will have implications on the cost and schedule.
As we can see, the scope of the project undergoes continuous elaboration, starting from the idea till the freezing of scope. It does not end there. The scope gets refined further and further throughout the project, and they are managed through change requests. Whether it is a single house or the largest airport in the world, the scope definition process remains the same, except in the change in magnitude of time, cost, scope and the number of stakeholders.
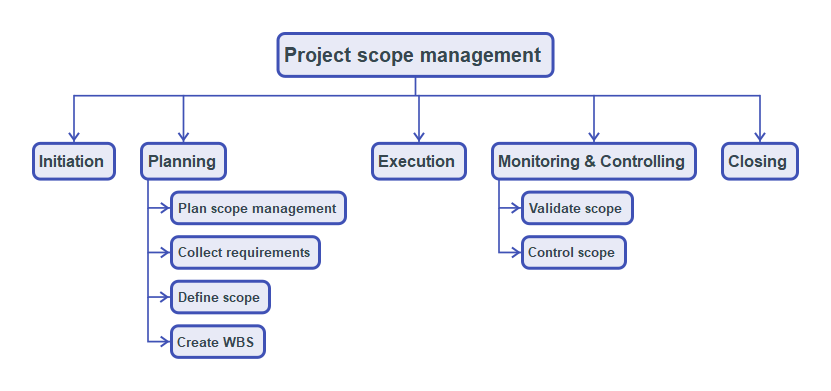
The process of defining and managing the scope of the project from initiation till the project close out comes under the purview of project scope management. The structured approach to project scope management as defined in the project management body of knowledge is depicted below in the Plan, Do, Check, Act (PDCA) cycle by Deming, which makes it much easier to understand and remember.
We start with planning for scope management, followed by Collecting requirements, Defining the scope and then Creating the Work Breakdown Structure (WBS). Scope validation happens while base-lining the scope and continues throughout the execution phase of the project. So, is the case with ‘Control’ scope.
Scope can be categorized into two types;
Product scope – Scope of the product to be delivered (Scope of the house)
Project scope – The work involved in delivering the product of the project (Work involved in constructing the house)
Commonly used tools and techniques;
- Expert judgment
- Data gathering
- Data analysis
- Meetings
- Decomposition
- Decision making
- Data representation
- Inter personal and team skills
- Context diagram
- Prototypes
- Inspection
- Product analysis
Common artifacts associated with Scope management
- Scope management plan
- Requirements management plan
- Requirements documentation
- Requirements traceability matrix
- Project scope statement
- Project documents updates
- Scope baseline (Project scope statement, Work Breakdown Structure (WBS), WBS Dictionary)
- Accepted deliverables
- Change requests
Reference
PMBOK V6 Page 130 – 171 Part 1 Guide
